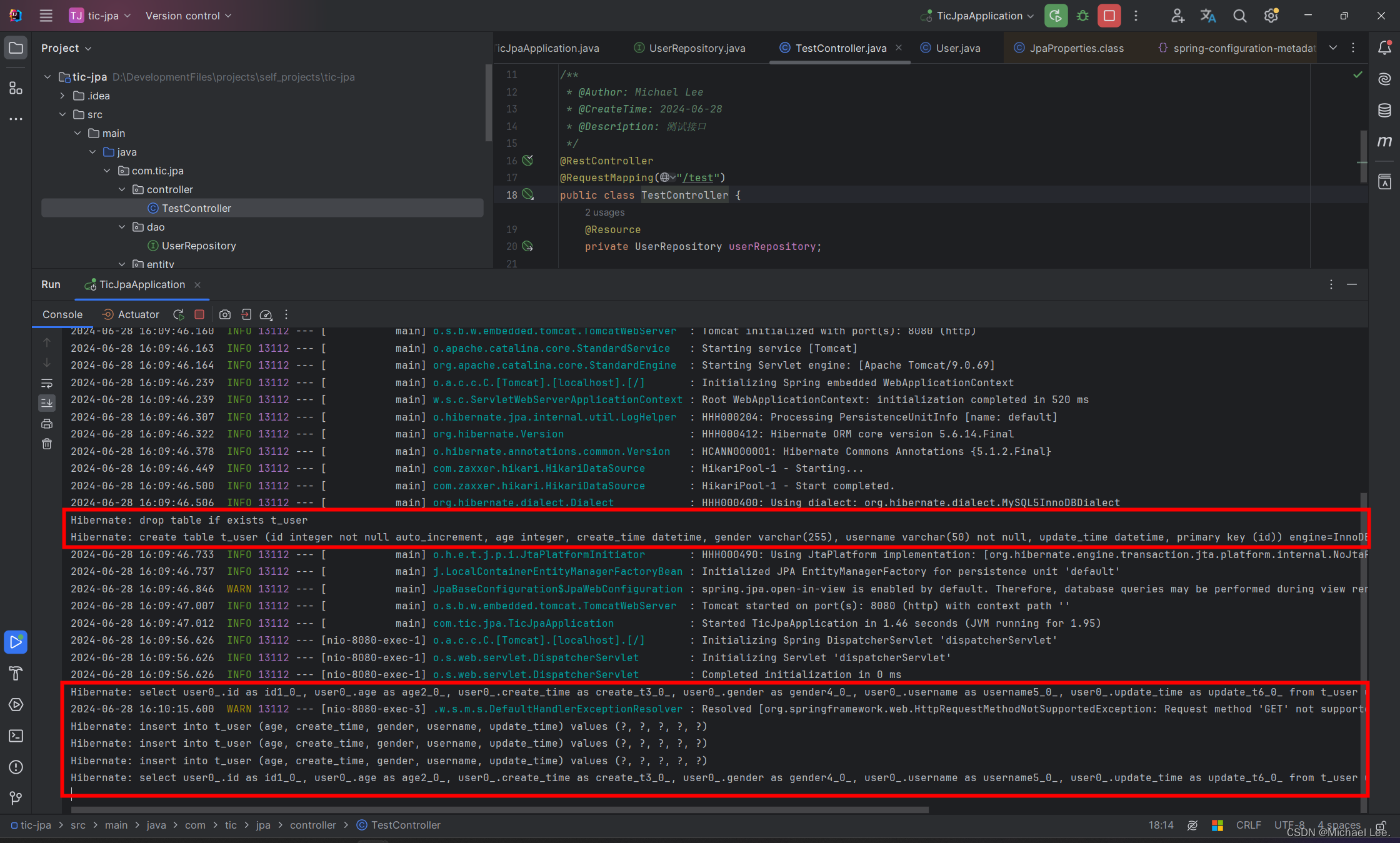
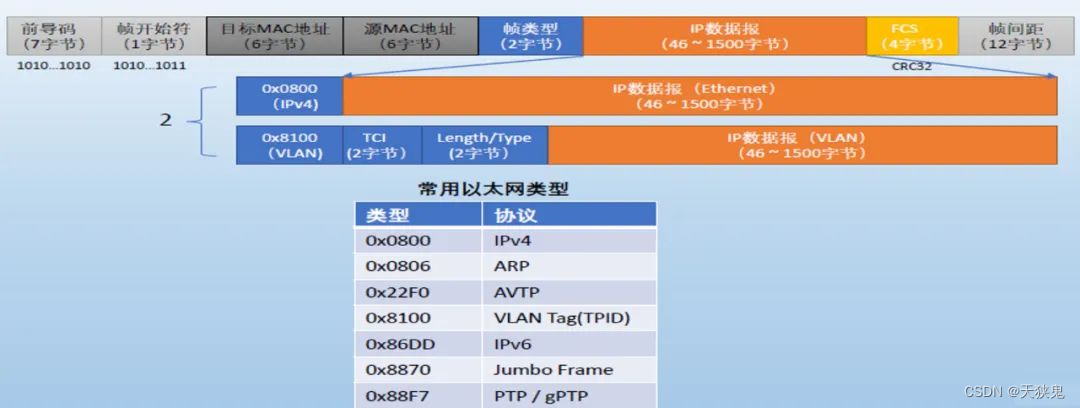
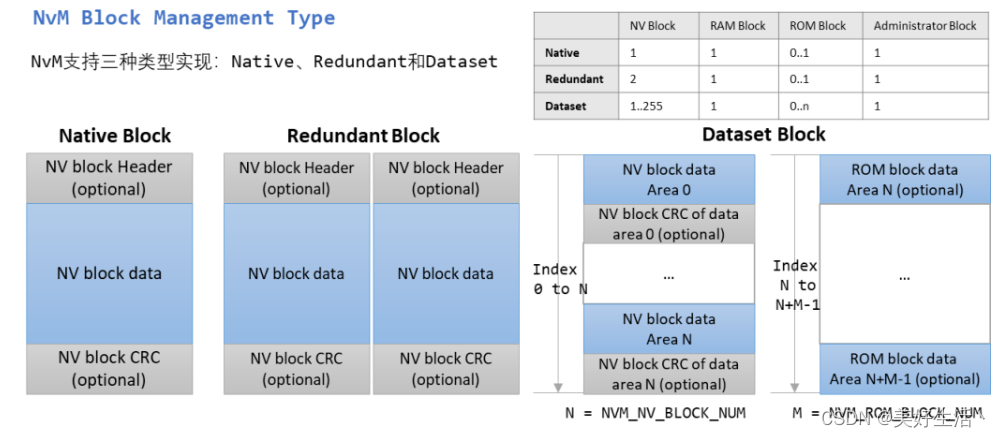
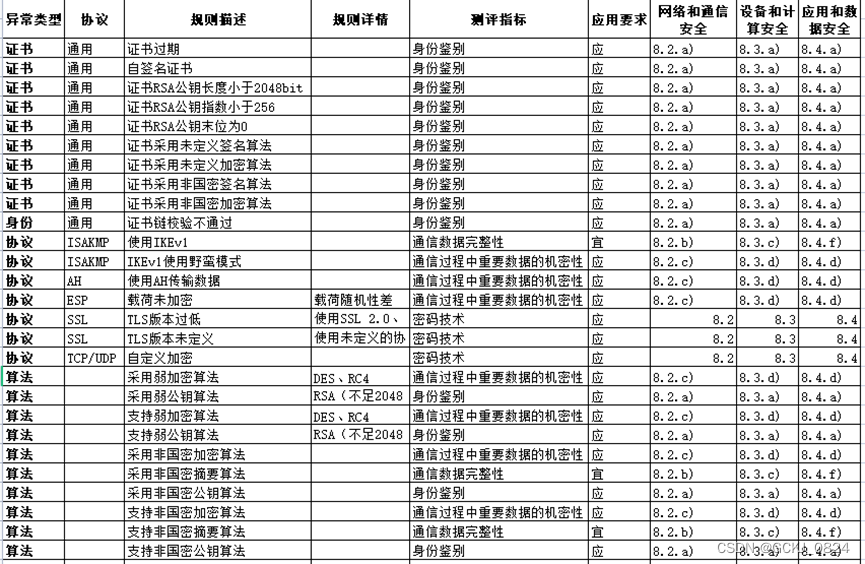
读写锁 RWMutex
写锁
加锁
RWMetex 的写锁复用了 Mutex:
// Lock locks rw for writing.
// If the lock is already locked for reading or writing,
// Lock blocks until the lock is available.
func (rw *RWMutex) Lock() {
if race.Enabled {
_ = rw.w.state
race.Disable()
}
// First, resolve competition with other writers.
// writer加锁
rw.w.Lock()
// Announce to readers there is a pending writer.
// 反转 readerCount,告诉 reader 有writer竞争锁
// Add(-rwmutexMaxReaders) 将 readerCount 置为负数,表示当前有 writer 竞争锁
r := rw.readerCount.Add(-rwmutexMaxReaders) + rwmutexMaxReaders
// Wait for active readers.
// 当前有 reader 持有锁,writer 等待
if r != 0 && rw.readerWait.Add(r) != 0 {
runtime_SemacquireRWMutex(&rw.writerSem, false, 0)
}
if race.Enabled {
race.Enable()
race.Acquire(unsafe.Pointer(&rw.readerSem))
race.Acquire(unsafe.Pointer(&rw.writerSem))
}
}
解锁
解锁也是复用的 Mutex,区别在于解锁的时候会唤醒所有阻塞的 reader。
// Unlock unlocks rw for writing. It is a run-time error if rw is
// not locked for writing on entry to Unlock.
//
// As with Mutexes, a locked RWMutex is not associated with a particular
// goroutine. One goroutine may RLock (Lock) a RWMutex and then
// arrange for another goroutine to RUnlock (Unlock) it.
func (rw *RWMutex) Unlock() {
if race.Enabled {
_ = rw.w.state
race.Release(unsafe.Pointer(&rw.readerSem))
race.Disable()
}
// Announce to readers there is no active writer.
// 反转 readerCount,告诉 reader 没有 writer 竞争锁
r := rw.readerCount.Add(rwmutexMaxReaders)
if r >= rwmutexMaxReaders {
race.Enable()
fatal("sync: Unlock of unlocked RWMutex")
}
// Unblock blocked readers, if any.
// 唤醒所有阻塞的 reader
for i := 0; i < int(r); i++ {
runtime_Semrelease(&rw.readerSem, false, 0)
}
// Allow other writers to proceed.
// writer 解锁
rw.w.Unlock()
if race.Enabled {
race.Enable()
}
}
读锁
加锁
// RLock locks rw for reading.
//
// It should not be used for recursive read locking; a blocked Lock
// call excludes new readers from acquiring the lock. See the
// documentation on the RWMutex type.
func (rw *RWMutex) RLock() {
if race.Enabled {
_ = rw.w.state
race.Disable()
}
// writer 加锁时,readerCount 是负数
// 写锁优先级比读锁高,reader 休眠
// 如果 reader+1 > 0, 当前加了读锁
if rw.readerCount.Add(1) < 0 {
// A writer is pending, wait for it.
runtime_SemacquireRWMutexR(&rw.readerSem, false, 0)
}
if race.Enabled {
race.Enable()
race.Acquire(unsafe.Pointer(&rw.readerSem))
}
}
解锁
// RUnlock undoes a single RLock call;
// it does not affect other simultaneous readers.
// It is a run-time error if rw is not locked for reading
// on entry to RUnlock.
func (rw *RWMutex) RUnlock() {
if race.Enabled {
_ = rw.w.state
race.ReleaseMerge(unsafe.Pointer(&rw.writerSem))
race.Disable()
}
// 有等待的 writer
if r := rw.readerCount.Add(-1); r < 0 {
// Outlined slow-path to allow the fast-path to be inlined
rw.rUnlockSlow(r)
}
if race.Enabled {
race.Enable()
}
}
func (rw *RWMutex) rUnlockSlow(r int32) {
if r+1 == 0 || r+1 == -rwmutexMaxReaders {
race.Enable()
fatal("sync: RUnlock of unlocked RWMutex")
}
// A writer is pending.
// 读锁全部解锁完毕,唤醒 writer
if rw.readerWait.Add(-1) == 0 {
// The last reader unblocks the writer.
runtime_Semrelease(&rw.writerSem, false, 1)
}
}
小结
sync.RWMutex复用sync.Mutex。- 写锁:
- 加锁时 writer 反转 readerCount 置为负数,如果当前有 reader 正在执行, readerCount 赋值给 readerWait,writer 休眠。
- 解锁时 writer 反转 readerCount 置为正常,并唤醒所有阻塞的 reader。
- 读锁:
- 加锁时 readerCount + 1,如果 readerCount < 0,reader 阻塞。
- 解锁时 readerCount - 1,如果 readerCount < 0,readerWait - 1,当 readerWait == 0 时,唤醒 writer。
sync.RWMutex 复用 sync.Mutex 。
- 调用 sync.RWMutex.Lock 尝试获取写锁时;
- 每次 sync.RWMutex.RUnlock 都会将 readerCount 其减一,当它归零时该 Goroutine 会获得写锁;
- 将 readerCount 减少 rwmutexMaxReaders 个数以阻塞后续的读操作;
调用 sync.RWMutex.Unlock 释放写锁时,会先通知所有的读操作,然后才会释放持有的互斥锁;
读写互斥锁在互斥锁之上提供了额外的更细粒度的控制,能够在读操作远远多于写操作时提升性能。




![[AHK]微信表情快捷输入](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6fc56df3390b42faa98c2901cdf1f6e7.png)